So finden Sie Wahrscheinlichkeiten für Z mit der Z-Tabelle
Sie können die Z -Tabelle verwenden, um einen vollständigen Satz von „weniger als“ Wahrscheinlichkeiten für einen weiten Bereich von z -Werten zu finden. Um die Z- Tabelle zu verwenden, um Wahrscheinlichkeiten für eine statistische Probe mit einer Standard-Normal (Z-) Verteilung zu finden, gehen Sie wie folgt vor:
Schneiden sich die Zeile und Spalte von Schritt 1 und 2.
Dieses Ergebnis stellt p (Z < z ), the probability that the random variable Z is less than the value z (also known as the percentage of z -values that are less than the given z value ).
Zum Beispiel: Angenommen, Sie wollen p (Z finden < 2.13). Using the Z -table below, find the row for 2.1 and the column for 0.03. Intersect that row and column to find the probability: 0.9834. Therefore p (Z < 2.13) = 0.9834.
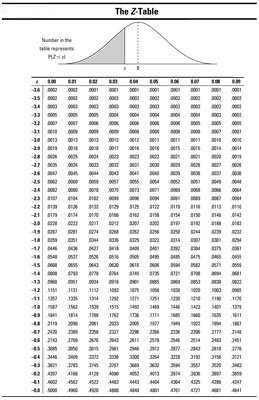
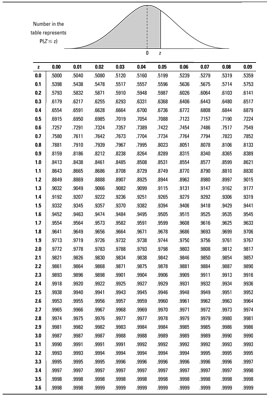
Feststellung, dass der Gesamtfläche unter alle Normalkurve (einschließlich der Standardnormalkurve) 1 ist, folgt, daß p (Z < 2.13) + p (Z > 2.13) = 1 ist. Daher p (Z> 2,13) = 1 - P (Z < 2.13) which equals 1 – 0.9834 which equals 0.0166.
Angenommen, Sie für p suchen möchten (Z < –2.13). You find the row for –2.1 and the column for 0.03. Intersect the row and column and you find 0.0166; that means p (Z < –2.13)=0.0166. Observe that this happens to equal p (Z >+2,13) .Der Grund hierfür ist ‚, weil die Normalverteilung symmetrisch ist. So ist der Schwanz der Kurve unterhalb -2.13 darstellt p (Z < –2.13) looks exactly like the tail above 2.13 representing p (Z > +2.13).